Table of Contents
Introduction
Choosing the right sleeping position is the secret key to a peaceful night’s sleep. Are you aware that your sleeping position is affected by gravity? Gravity determines people’s comfort level in different sleeping positions and also affects blood flow. In this blog, we are going to see sleeping positions for 28 dis-eases with some tips and benefits of sleep posture.
Why does sleep position matter?
Can you believe choosing the right sleep position can help prevent and manage certain dis-eases? Yes, it’s true.
Apart from maintaining your spine alignment and providing pain relief, selecting the right sleep position improves your brain health by removing waste from the brain and preventing certain dis-eases and also has some therapeutic aspects.
Gravity and sleep position
The duration and quality of sleep are affected by how gravitational force acts on our body. When we lie down, gravity pulls our body downwards, which affects the alignment of the spine and joints, blood flow, breathing and distribution of our body weight.
So, the way we sleep can affect how well we sleep and it can help us prevent and manage certain dis-eases.
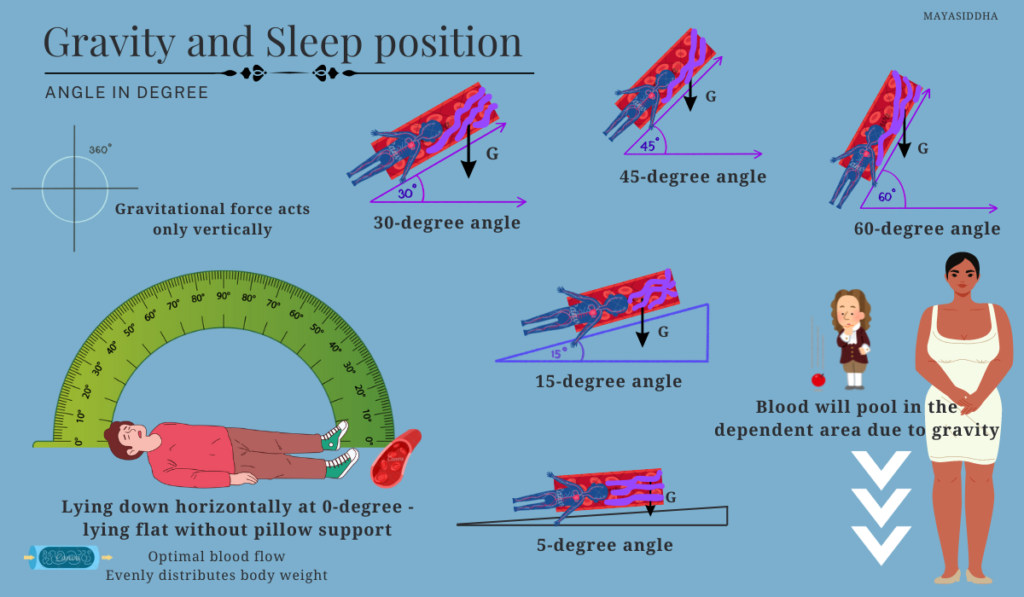
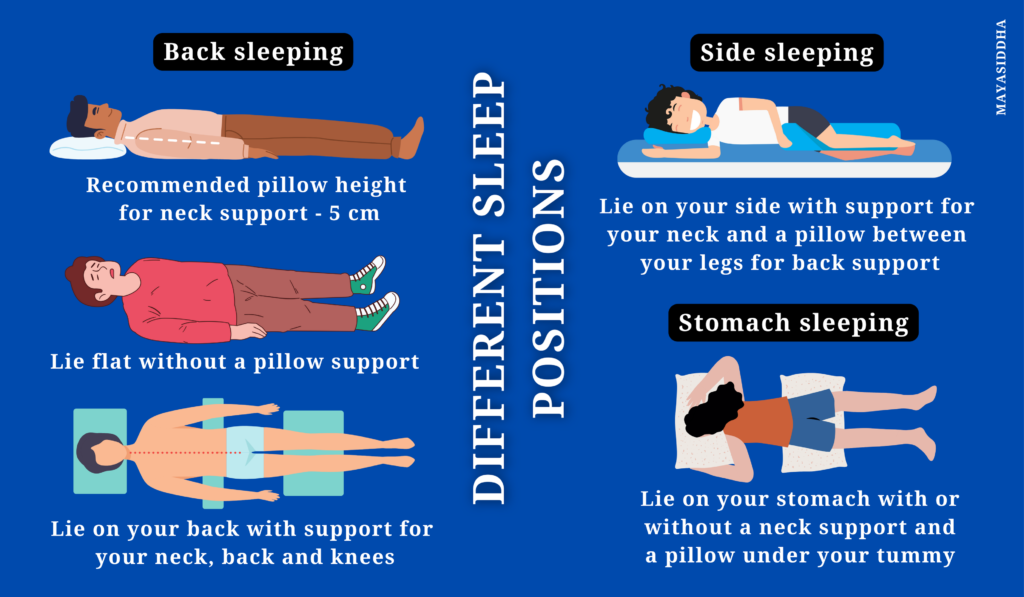
Ideal sleep position & Benefits of sleep posture
There are three sleep positions and each position has different benefits-
- Side sleep position (Lateral sleep position) – right and left side
- Back sleep position (Supine sleep position)
- Stomach sleep position (Prone sleep position)
Speaking of truth, there is no one ideal sleep position, you have to try different sleep positions and pillow adjustments until you find the one that works. However, Side sleeping and back sleeping are considered the best sleeping positions, but not for all.
Benefits of Side-sleeping
- Clears away waste from the brain.
- Prevents neurodegenerative dis-eases.
- Improves blood flow.
- Reduces acidity.
- Relieves gallstone pain.
- Eases the passage of kidney stones.
- Good sleep position for Elders.
- Prevents and helps to manage Alzheimer’s dis-ease (a condition with reduced intellectual ability and memory loss).
- Good for people suffering from Tuberculosis.
- Keeps airway open thus reducing snoring.
- Good for people with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (a condition where breathing stops temporarily during sleep).
- Lowers stress levels and makes people with heart failure feel very comfortable in this sleep position.
- Takes away the pressure from the liver and large blood vessels.
Benefits of Back-sleeping
- Facilitates recovery from illness.
- Maintain spine alignment.
- Takes away stress on the neck and back.
- Reduces eye pressure thus good for people with Glaucoma (a condition that can cause blindness).
- Reduces stress level.
- Promotes a state of calmness.
- Reduces stress on the heart.
- Highly recommended for people with Asthma.
- Highly recommended sleep position for babies.
- Improves blood flow to the brain for people experiencing ischemic stroke within a 12-hour window.
- Optimal blood flow to the brain.
- Equal blood flow to each kidney in a healthy person.
- Gravity ensures that blood flows evenly to all organs.
- Evenly distributes body weight.
Benefits of Stomach sleeping
- Improves oxygen flow to the lungs.
- Reduces snoring.
Sleep position I recommend for a Physically well person
A person can’t maintain a single sleep position, unconsciously a person can shift from one position to another. So I recommend practising sleeping on the side and back. If you don’t have any breathing issues try avoiding the stomach sleep position.
But keep in mind comfort is important while choosing a sleep position.
How to sleep:
Recommended pillow size for neck support: For optimal sleep, it’s important to choose the right pillow size to ensure proper neck support.
For back sleeping, experts recommend using a pillow with a height of about 5 cm. For side sleeping, use a firm pillow that fits the width of your neck and shoulder. This height helps maintain the natural alignment of your spine, reducing strain and promoting better sleep quality.
Back sleeping:
Option 1. Lie flat on your back without a pillow support. Keep your hands straight alongside your body and position your legs symmetrically to maintain proper spine alignment.
Option 2. Lie on your back with pillow support to the neck and place a thin, soft cloth under the arch of your back and knees for comfort.
Side sleeping:
Option 1. Turn to your left side. Fold your left arm and tuck it under your head for support. Bend your left leg slightly and place your right leg straight over it. Keep your right hand straight and place it over the right side of the body.
Option 2. Use a firm pillow that fits the width of your neck and shoulder. Additionally, place a thin pillow between your legs that matches the distance between them while standing for comfort and spine alignment while lying down.
benefits of sleep posture.
Stomach sleeping:
Lie on your stomach without a pillow for neck support. Instead, place a thin pillow under your tummy for back support. Turn your head to either side and place your hands symmetrically.
Sleep positions for different conditions
1. Sleep Position for Babies up to 1 year old
Babies up to 1 year old should be placed in the Back sleeping position to avoid the unexpected and unexplained death of a healthy baby (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome/Cot death).
Sleep position to avoid for babies: Babies shouldn’t be placed on their stomachs which is a high-risk position to cause Cot death.
| Indians place their babies in cradles made from saree which prevents babies from falling into a stomach sleeping position and reduces the risk of flat head formation when babies are placed on flat surfaces. |
benefits of sleep posture.
If babies roll onto their stomachs, reposition them onto their backs. However, if they roll onto their sides on their own, there is no need to reposition them.
But babies can be placed on stomach position if they are dealing with certain breathing issues. Please consult with the Doctor.
2. Sleep Position for children and adults to improve Brain Health
Brain detoxing position: Sleeping on the side increases waste clearance from the brain thus improving the brain’s health and protecting the brain from certain dis-eases.
Optimal blood flow position: Sleeping on the back maintains healthy blood flow to the brain without collapsing the blood vessels.
benefits of sleep posture.
3. Sleep position for Elders
As we age, spine flexibility reduces, so elders find side sleeping is comfortable. As this is the brain detox position, it helps prevent age-related brain health issues.
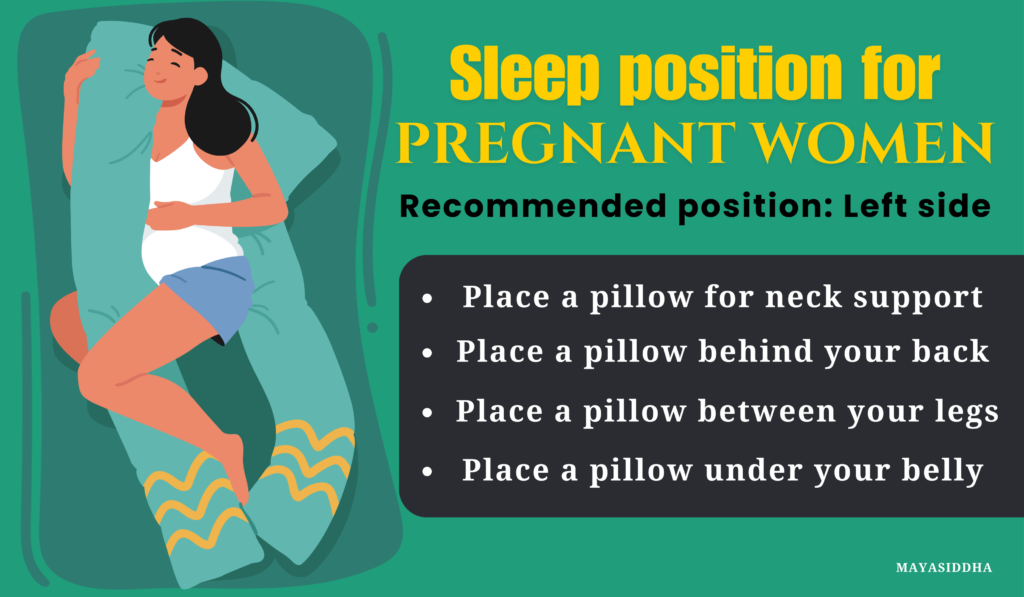
4. Sleep position for Pregnant women
First trimester: Pregnant women for the first 3 months can sleep on their back or side, but avoid stomach sleeping.
Second and Third trimesters: From the start of the 4th month to until delivery, pregnant women should sleep on their side, preferably the left side, as it improves blood flow to the baby.
Sleeping on the back will compress the large blood vessels, which reduces blood flow and increases leg swelling and sleeping on the right side will put pressure on the liver which does major functions including detoxification.
How to sleep comfortably with a pregnant belly: Place a pillow behind your back and another between your legs to relieve stress on the back. Additionally, use a pillow under the belly for extra support.
5. Sleep position for Alzheimer’s dis-ease
benefits of sleep posture.
Alzheimer’s dis-ease is caused by the accumulation of waste in the brain. Research proved that side sleeping effectively clears away the waste from the brain. Thus, sleeping on the side will help prevent and manage this condition.
When sleeping on your left side, the blood vessel in your neck that removes waste from the brain stays wide open, while the vessel on the right side collapses. The opposite happens when you sleep on your right side.
Research says this mechanism is effective in waste clearing and is the natural body’s mechanism to prevent neuro-degenerative dis-eases like Alzheimer’s. So, sleeping on both sides – right and left helps prevent and manage this condition.
6. Sleep position to prevent insufficient blood flow to the brain (Ischemia)
Maintaining a proper head position is important during sleep. Sleeping on the back while keeping the head flat provides sufficient blood flow to the brain in a healthy person.
7. Sleep position and first aid position for Ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke is a condition that causes stroke due to insufficient blood flow to the brain which can be due to blockage in the blood vessels or inadequate sleep.
First aid position: To prevent, sleep on the back and if you are suffering from this condition, as a first aid laying down that person flat on the back within a 12-hour window increases blood flow to the brain where it lacks blood.
Sleep position: Sleeping on the back provides sufficient blood flow and sleeping on the side clears away waste. Try adapting these two positions throughout the night. Clear the underlying root cause of this condition to have a restful sleep.
8. Sleep position for Neck pain
Sleeping on the back with and without support to the neck takes away stress on the neck. Lying flat without neck support takes time to adapt to this position, but I recommend this position. If you need neck support, place a thin and firm pillow under your head and neck. The recommended pillow height is 5 cm.
Sleeping on the side will also relieve stress on the neck. While sleeping on the side keep your head aligned with your spine, don’t bend your neck forward or backwards it will cause pain. Choosing a firm pillow that fits the width of your neck and shoulder provides the necessary support. Too soft or too thick pillows lead to discomfort and cause neck pain.
9. Sleep position for Back pain
Sleeping on the back with and without support takes away stress on the back. Lying flat without back support takes time to adapt to this position, but I recommend this position. If you need back support, place a soft pillow or cotton cloth under the arch of your back and knees.
Sleeping on your side can help relieve stress on your back. To achieve this, use a firm pillow under your head and another one between your legs. The pillow between your legs should be as thick as the space between your legs when you stand upright. Position the pillow from your knees to your ankles for the best support.
10. Sleep position for Shoulder pain
Sleeping on the back helps reduce shoulder pain. Side sleeping will increase shoulder pain. It’s fine to lie flat without a pillow, but if you prefer a pillow, a 5 cm pillow is recommended.
11. Sleep position for Glaucoma
Increased eye pressure is one of the causes of Glaucoma. If you are suffering from Glaucoma, sleeping on the back helps manage it. But lying flat will increase the eye pressure thus increasing the glaucoma symptoms.
Head-up tilt position: Lie flat on the bed which is tilted at a 5-degree angle.
Prop your head: Raise your head and shoulder to a 30-degree angle using a wedge pillow designed for that angle.
These two positions will reduce eye pressure and help manage glaucoma.
12. Sleep position for Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition where you hear noises that don’t come from outside sources. It can arise from various factors including increased pressure in the brain, sinus problems and sleep deprivation.
Sleeping on your back with your head and shoulder elevated at a 30-degree angle can lessen brain pressure, relieve stuffy nose, and ease tinnitus symptoms, promoting better sleep.
13. Sleep position for Stuffy Nose
Lying flat can increase the blockage in the nose. Sleeping on your back with a raised head and shoulder can clear blockage in the nose and improve your sleep.
14. Sleep position for Snorers
Lying on the back increases snoring, because of the gravity. When lying on the back, your tongue due to gravity falls back and blocks the airway which causes sound sleeping.
Sleeping on your side shifts the tongue to the side, preventing airway blockage, thus reducing snoring and making you sleep better.
15. Sleep position for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea occurs when the airway becomes blocked multiple times during sleep, which reduces or completely stops airflow. Age and being overweight are some of the reasons for sleep apnea. Heavy snoring is a symptom of this condition.
Sleeping on the side keeps the airway open thus reducing sleep apnea and improving sleep quality.
16. Sleep position for Cough
The cough mechanism is naturally reduced during sleep. But due to some conditions like colds and other lung dis-eases, cough is produced during sleep.
Sleeping on the side reduces cough. Sleeping on the back with an elevated head and chest reduces cough. Research shows elevating the head and chest at a 60-degree angle with a wedge pillow of that angle eases the cough without pain.
17. Sleep position for Asthma
Studies show sleeping on the side increases asthma symptoms. Sleeping on the back reduces asthma symptoms day by day. People with asthma should sleep on their backs with and without pillow support according to their comfort.
18. Sleep position for Tuberculosis
Some people have Tuberculosis (TB) in both lungs while others have TB in one lung. People with TB in one lung should sleep on the side to avoid TB spreading to the healthy lung.
How to sleep with TB in one lung: If you have a TB infection in the right lung, you should sleep on the right side to avoid infection spreading to the healthy left lung and vice versa. But the further infection spread on the right lung can’t be avoided.
When you have a TB infection in one lung, it is recommended to sleep on the same side, with the infected lung facing downwards to save the healthy lung.
People with TB infection in both lungs are advised to sleep on the more infected side. That person can turn to the opposite side at intervals for comfort.
19. Sleep position for Pneumonia
Some people have Pneumonia infection in one lung and some have it in both lungs. People with this infection have trouble breathing.
If you have Pneumonia infection in your right lung, you should sleep on the left side, it increases oxygen flow and improves the condition of the right lung, but worsens the healthy left lung and vice versa. The rule is “Good side down”.
How to sleep with Pneumonia: Start by sleeping on the stomach, it increases the oxygen level. Sleep in the stomach position for 30 minutes to 2 hours as per your comfort. Then you can switch to your side with the “good side down”.
Throughout the night you can switch between these two positions, it will help you sleep. But without clearing the root cause sleep will not be entirely restful.
20. Sleep position for Breathlessness
If you have trouble breathing, then you have to try stomach sleeping. Lay flat on the stomach without pillow support on the firm mattress or surface. It increases oxygen level within 30 minutes of adapting to this position. But clear the underlying causes of breathing trouble.
21. Sleep position for High blood pressure
Studies show that back sleeping can increase blood pressure during sleep. Most people with high blood pressure also experience sleep apnea, so side sleeping will be better for them.
Sleeping on either side is recommendable. Along with high blood pressure, if you deal with acidity choose the left side and if you deal with heart dis-ease choose the right side.
22. Sleep position for Heart failure
Studies have shown that individuals with heart failure tend to avoid sleeping on their left side and predominantly favour the right side. Right-side sleeping is found to lower stress levels, making it a comfortable option for people with heart failure.
23. Sleep position for Peripheral Artery Dis-ease
Peripheral artery dis-ease is a condition in which blood circulation is poor in arms or legs. Back sleeping evenly distributes weight and provides sufficient blood flow to all body parts.
Sleeping like a chimpanzee can help you sleep with peripheral artery dis-ease. Lie on your back and slightly elevate your head, shoulder and legs at a 5-degree angle to facilitate blood flow. But without treating the root cause sleep will not be restful and easy.
24. Sleep position for Acidity
benefits of sleep posture.
Picture your stomach as a box and your food pipe as a tube connected to the upper right corner of the box. Fill half of the box with water. When you tilt the water-filled box to the right, the water flows back into the tube. However, tilting it to the left keeps the water inside the box without any backflow.
Similarly, your food pipe is connected at the top of your stomach, which is located on the upper left side of your belly. Sleeping on your left side helps prevent acid from flowing back into the food pipe.
Sleeping on your right side and lying flat on your back increases acidity. However, lying on your back with a slightly elevated upper body at a 5-degree angle can help reduce acidity.
25. Sleep position for Gallstone pain
Sleeping on the left side takes away the pressure from the liver, thus reducing gallstone pain. However, without treating it, pain will reappear.
26. Sleep position for Kidney stone
While talking about kidney stones, there are two scenarios – people with kidney stones and people who are at risk of developing kidney stones.
People with kidney stones: If you have kidney stones on your right kidney, sleep on your right side and vice versa. Sleeping on the same side where the kidney stone is located, facilitates the passage of the kidney stone.
If you have kidney stones on both kidneys, then sleep flat on your back. Sleeping on the back evenly distributes blood flow to both kidneys which helps in the passage of the stones.
People who are at risk of developing kidney stones: If you are at risk of developing kidney stones on the right kidney, sleep on your left side and vice versa. Sleeping on the opposite side helps prevent the development of kidney stones when you are at risk.
27. Sleep position for Piles and Anal fissure pain
Sleeping on the left side with a pillow in between legs helps relieve pain. Sleeping on the stomach with a soft and thin pillow under your tummy also helps relieve pain.
28. Sleep position for Swelling in legs, ankles and Varicose vein
Sleeping on your back with your legs elevated at a 15-degree angle facilitates blood flow and reduces swelling. Stay in this position for 20-30 minutes initially. Then, lower the angle to 5 degrees for comfortable sleep throughout the night while still enjoying the benefits.

benefits of sleep posture.

Disclaimer
According to your medical conditions make sure to consult a Doctor before adapting to this sleep position. Nothing on this blog is intended to be a substitute for Professional Medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Keep in mind without clearing the root cause of the di-ease, sleep will not be completely restful.
Reference
benefits of sleep posture.
1. Reddy, O. C. (2020). The Sleeping Brain: Harnessing the Power of the Glymphatic System through Lifestyle Choices. Brain Sciences, 10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10110868.
benefits of sleep posture.
2. Simadibrata, D. M., Lesmana, E., Amangku, B. R., Wardoyo, M. P., & Simadibrata, M. (2023). Left lateral decubitus sleeping position is associated with improved gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Journal of Clinical Cases, 11(30), 7329-7336. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7329.
3. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Choosing the Best Sleep Position. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/choosing-the-best-sleep-position#:~:text=Positioning%20yourself%20on%20your%20side,make%20symptoms%20worse%2C%20Salas%20says.
4. Danielle Pacheco, Ealena Callender. (2024 March 27). Pregnancy Sleep Positions. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/pregnancy/pregnancy-sleep-positions.
5. Mayo Clinic. (2024 January 19). Sleeping positions that reduce back pain. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/in-depth/sleeping-positions/art-20546852.
6. Leung, R. S., Bowman, M. E., Parker, J. D., Newton, G. E., & Bradley, T. (2003). Avoidance of the left lateral decubitus position during sleep in patients with heart failure: Relationship to cardiac size and function. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 41(2), 227-230. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(02)02717-1.
7. Schwartz, B. F., Dykes, T. E., Rubenstein, J. N., Stackhouse, G. B., & Stoller, M. L. (2007). Effect of body position on renal parenchyma perfusion as measured by nuclear scintigraphy. Urology, 70(2), 227–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2007.03.057.
8. Shekarriz, B., Lu, H. F., & Stoller, M. L. (2001). Correlation of unilateral urolithiasis with sleep posture. The Journal of urology, 165(4), 1085–1087.
9. Ziaee, S. A., Moradi, A., Fateh, M., & Moghaddam, S. M. (2008). Sleep posture and unilateral renal stone formation. Scandinavian journal of urology and nephrology, 42(6), 551–554. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365590802201243.
10. Chi, T., & Stoller, M. L. (2011). STONES: Passing a stone in your sleep might be easier than you think. Nature Reviews. Urology, 8(10), 533. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2011.126.
11. Naughton, M. T., & Lorenzi-Filho, G. (2009). Sleep in heart failure. Progress in cardiovascular diseases, 51(4), 339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2008.02.001.
12. Tetley, M. (2000). Instinctive sleeping and resting postures: An anthropological and zoological approach to treatment of low back and joint pain. BMJ : British Medical Journal, 321(7276), 1616-1618. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.321.7276.1616.
13. Helm, W. H. (1951). The Importance of Sleeping Posture in the Spread of Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Thorax, 6(4), 417-425. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.6.4.417.
14. Park, J. H., Yoo, C., Yoo, E., & Kim, Y. Y. (2019). Intraocular Pressure Elevation during Lateral Body Posture in Side-sleeping Glaucoma Patients. Optometry and vision science : official publication of the American Academy of Optometry, 96(1), 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1097/OPX.0000000000001322.
15. Sedgewick, J. H., Sedgewick, J. A., Sedgewick, B. A., & Ekmekci, B. (2018). Effects of different sleeping positions on intraocular pressure in secondary open-angle glaucoma and glaucoma suspect patients. Clinical Ophthalmology (Auckland, N.Z.), 12, 1347-1357. https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S163319.
16. Yeon, Y., Yoo, C., Lee, E., Park, H., & Kim, Y. Y. (2014). Effects of head elevation on intraocular pressure in healthy subjects: Raising bed head vs using multiple pillows. Eye, 28(11), 1328-1333. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.211.
17. Olavarría, V. V., Lavados, P. M., Muñoz-Venturelli, P., González, F., Gaete, J., Martins, S., Arima, H., Anderson, C. S., & Brunser, A. M. (2017). Flat-head positioning increases cerebral blood flow in anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke. A cluster randomized phase IIb trial. International Journal of Stroke. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493017711943.
18. Simka, M., Czaja, J., & Kowalczyk, D. (2019). Collapsibility of the internal jugular veins in the lateral decubitus body position: A potential protective role of the cerebral venous outflow against neurodegeneration. Medical hypotheses, 133, 109397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109397.
19. Moon, R. Y., Carlin, R. F., Hand, I., & TASK FORCE ON SUDDEN INFANT DEATH SYNDROME AND THE COMMITTEE ON FETUS AND NEWBORN (2022). Sleep-Related Infant Deaths: Updated 2022 Recommendations for Reducing Infant Deaths in the Sleep Environment. Pediatrics, 150(1), e2022057990. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2022-057990.
20. Infant sleep position and SIDS. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
21. (2009). Glas. Srpska akademija nauka i umetnosti. Odeljenje medicinskih nauka, (50), 125–137.
22. Tsai, C., Nagata, T., Liu, C., Suganuma, T., Kanda, T., Miyazaki, T., Liu, K., Saitoh, T., Nagase, H., Lazarus, M., Vogt, K. E., Yanagisawa, M., & Hayashi, Y. (2021). Cerebral capillary blood flow upsurge during REM sleep is mediated by A2a receptors. Cell Reports, 36(7), 109558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109558.
23. Klingelhöfer, J. (2012). Cerebral blood flow velocity in sleep. Perspectives in Medicine, 1(1-12), 275-284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.permed.2012.02.021.
24. Leung, R. S., Bowman, M. E., Parker, J. D., Newton, G. E., & Bradley, T. (2003). Avoidance of the left lateral decubitus position during sleep in patients with heart failure: Relationship to cardiac size and function. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 41(2), 227-230. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(02)02717-1.
25. Kalolella, A. B. (2016). Sleeping position and reported night-time asthma symptoms and medication. The Pan African Medical Journal, 24. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2016.24.59.9159.
26. Sato, S., Saito, J., Fukuhara, A., Uematsu, M., Suzuki, Y., Rikimaru, M., Kawamata, T., Umeda, T., Koizumi, T., Togawa, R., Sato, Y., Nikaido, T., Minemura, H., Kanazawa, K., Tanino, Y., & Shibata, Y. (2021). Association Between Sleep Characteristics and Asthma Control in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Asthma and Allergy, 14, 325-334. https://doi.org/10.2147/JAA.S301444.
27. Meli, A., Viñas, E. B., Battaglini, D., Bassi, G. L., Yang, H., Yang, M., Bobi, J., Motos, A., Fernández-Barat, L., Chiumello, D., Pelosi, P., & Torres, A. (2020). Lateral position during severe mono-lateral pneumonia: An experimental study. Scientific Reports, 10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76216-w.
28. Shapiro, Robert M.D.; Broccard, Alain M.D.. Patient Positioning in Respiratory Disease. Clinical Pulmonary Medicine 4(1):p 45-52, January 1997.
29. Berger, M., Oksenberg, A., Silverberg, D. S., Arons, E., Radwan, H., & Iaina, A. (1997). Avoiding the supine position during sleep lowers 24 h blood pressure in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients. Journal of human hypertension, 11(10), 657–664. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000510.
30. Ramtin Massoudi. (2024, March 20). Best Sleeping Position for Peripheral Artery Disease. Lavascular specialists. https://lavascularspecialists.com/blog/best-sleeping-position-for-pad/
31. Soe HZ. Review Article on Prevention and Treatment of Gallstones. Med J Clin Trials Case Stud 2023, 7(4): 000345.
32. Wieslander, B., Ramos, J. G., Ax, M., Petersson, J., & Ugander, M. (2019). Supine, prone, right and left gravitational effects on human pulmonary circulation. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-019-0577-9.
33. Peter Beaconsfield, Jican Ginsburg. Effect of Changes in Limb Posture on Peripheral Blood Flow
34. Martin Du Pan, Remy & Benoit, Raymond & Girardier, Lucia. (2004). The role of body position and gravity in the symptoms and treatment of various medical diseases. Swiss Medical Weekly. 134. 543-51. 10.4414/smw.2004.09765.
35. Gonfalone, A. A. (2018). Sleep and gravity. Medical Hypotheses, 113, 81-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2018.02.020.
36. Jay Summer, Dr. Lulu Guo. (2023, October 18). “How To Sleep with Tinnitus”: Sleep Foundation. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/physical-health/how-to-sleep-with-tinnitus.
37. Jay Summer, Dr. Abhinav Singh. (2023, April 27). “How To Sleep With A Stuffy Nose”: Sleep Foundation. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/physical-health/treatment-for-blocked-nose-at-night#elevate-your-head.
38. Danielle Pacheco, Dr. Abhinav Singh. (2024, January 5). “Best Sleeping Position for Sleep Apnea”: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleeping-positions/best-sleeping-position-for-sleep-apnea.
39. November. Insomnia in Tuberculosis. CHEST Journal.
40. Seo, K., & Cho, M. (2015). Analysis of the pulmonary functions of normal adults according to pillow height. Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 27(10), 3085-3087. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.27.3085.
McMullan, C. J., Curhan, G. C., & Forman, J. P. (2016). Association of short sleep duration and rapid decline in renal function. Kidney International, 89(6), 1324-1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2015.12.048.







6 Comments
Awesome posts
Thanks a lot for your thoughtful appreciation and I am happy that this content was useful to you.
I’m no longer certain the place you are getting your
information, however great topic. I must spend soje time learning much more or figuring out more.
Thanks for magnificent information I used to
be in sarch of this info forr my mission.
Just letting you know, I’ve cited all the references I used to gather the information presented above. Thank you.
Thank you for your valuable sharing sir.
In our books,sleeplessness in vadham kurai gunam,more sleep in iyam mighu gunam.anyway i gain more information thanks DR .