Introduction
It’s well known that the Sun emits radiation that affects the Earth and its residents. In this blog, we will explore what is Solar wind and how the Sun’s radiation a.k.a. Solar wind impacts the Earth.
Before diving into the blog, check into the concept of Magneto-dielectricity, as this is the heart of this blog and the key to understanding energy dynamics.
What is a Solar wind ?
The solar wind is a radiation thrown out by the sun. Radiation is nothing but the energy discharged from the core.
What is solar wind ? Simply put, Solar wind is the Sun’s magnetic field or Solar energy.
When I say “magnetic field”, most of my readers would probably think of atoms, electric fields and magnetic fields. But let’s set that aside for now because the magnetic fields of the Sun, Earth and Humans all work on the magneto-dielectricity principle.
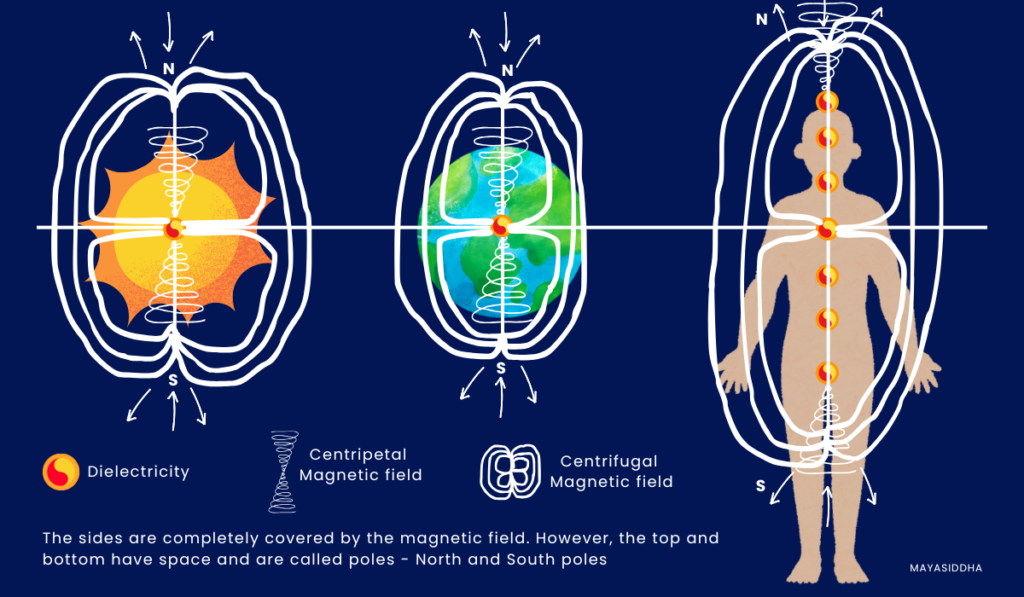
If you wanna learn about Magneto-dielectricity, the core concept of the universe, you can refer here. Now let’s see how solar wind impacts the Earth.
Offender: Solar wind
The Sun constantly radiates solar wind which strikes every planet. Throughout the solar cycle, the intensity of the solar wind fluctuates.
Defender: Earth’s magnetic field
Our Earth is so smart, that it uses its sunscreen i.e., Earth’s magnetic field to defend itself from this striking solar wind. What it does is, it just deflects the solar wind with its intact magnetic bubble* on the east and west sides. [NO ENTRY]
* Earth’s magnetic field = Geomagnetic field/Magnetosphere/ Magnetic bubble.
Offender-Defender interaction
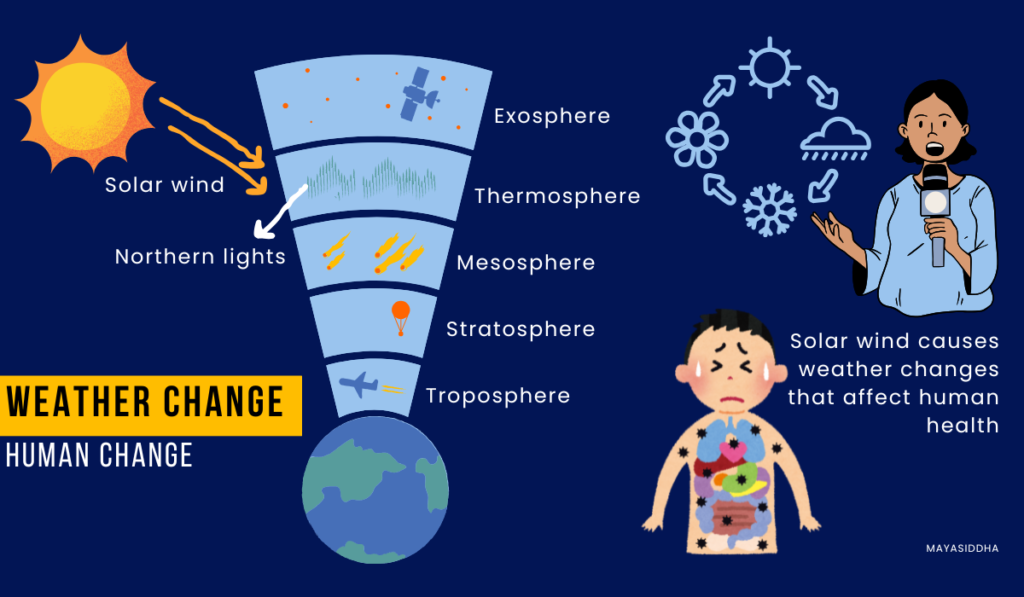
Even though Earth is so smart, it has forgotten about space on top and bottom. So, the deflected solar wind sneaks into the Earth via the north and south poles, causing the northern and southern lights. [EARTH’S ENTRANCE]
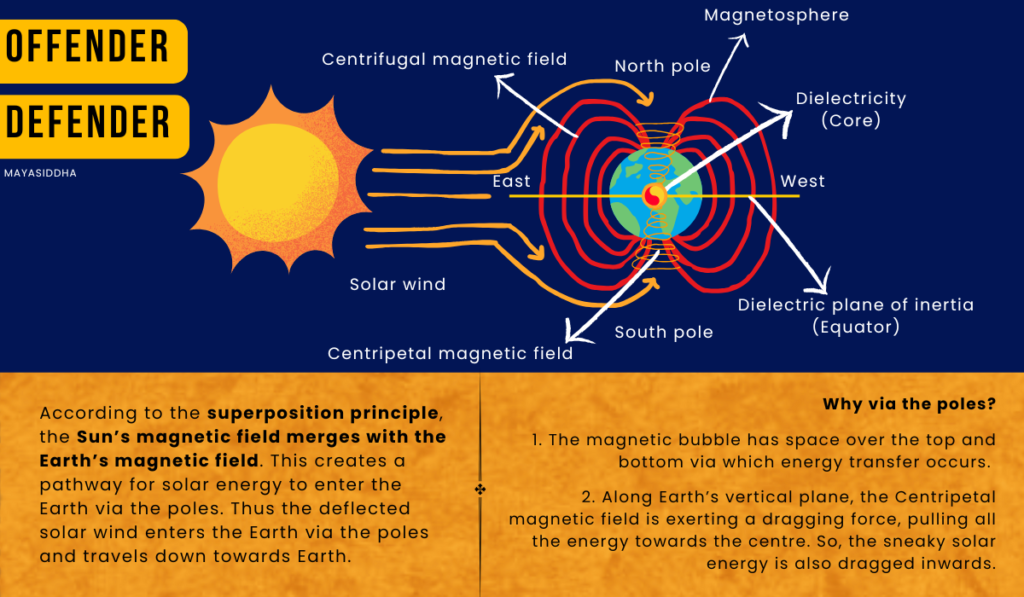
Offender – Solar wind and Defender – Magnetic bubble aren’t always on better terms; they often clash. So, what happens when they clash?
Battle between the Offender and Defender
Can Solar wind destroy Earth ? Let’s see.
SLINGSHOT: As the solar wind is constantly striking the magnetic bubble, it pushes the magnetic bubble on the nightside to stretch out like an elastic band in a slingshot, called Magnetotail.
When it becomes overstretched, it rebounds, pushing back the solar wind with force, which directs solar energy into the Earth via the poles called Substorm.
When the intensity of the offender – solar wind rises, it causes troubles, initiating a battle with the Earth’s defence.
INTENSE BATTLE: Whenever the solar wind intensifies, it hits the Geomagnetic field very hard, causing a disturbance in the magnetic bubble called a Geomagnetic storm/ Magnetic storm.
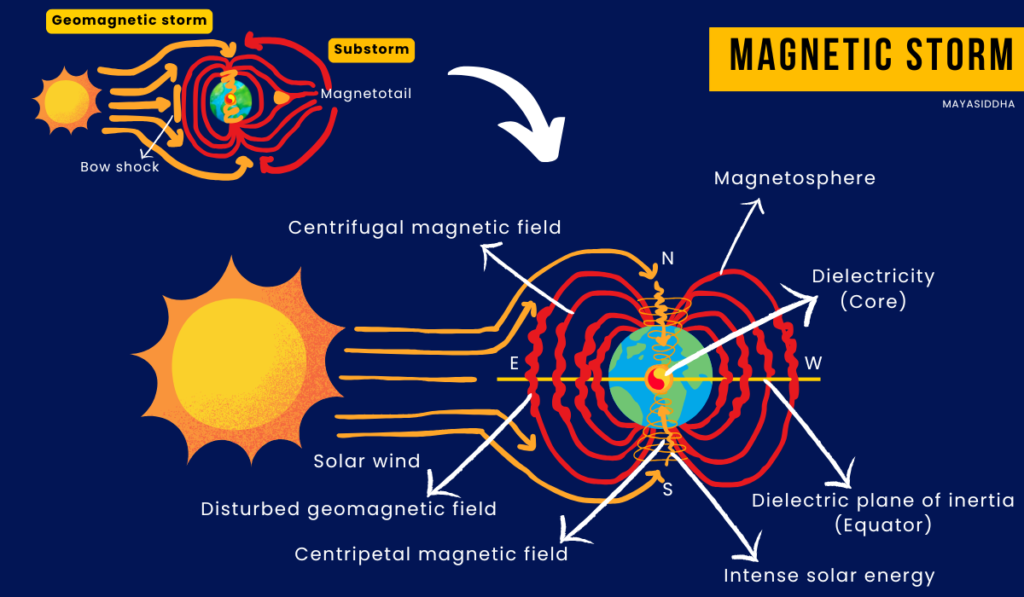
Substorm is like a small battle in between the intense battle. Substorms can occur several times a day whereas Magnetic storms can occur at any time during the solar cycle and last for several days. Each time a substorm occurs, it pushes the solar energy further down towards the Earth.
Since Earth and humans are solar dependent, any variation in the intensity of the solar wind can negatively impact our planet and us.
Impacts of the Solar wind on Earth
1. Disturbs the Geomagnetic field
During a magnetic storm, the intense solar wind creates a disturbance in the geomagnetic field, which in turn disturbs our magnetic field.
NOTE: Under normal conditions, solar wind doesn’t negatively impact Earth, but when its intensity rises, it does.
2. Causes a change in the Weather pattern
The solar wind that enters the Earth induces a change in weather patterns – Air pressure, Precipitation, Wind and Humidity. This weather change impacts our health.
Summary
Everything in this universe is Magneto-dielectricity. The solar magnetic field that emerges from the sun’s dielectric centre radiates out into interplanetary space and strikes all the planets. Likewise, the Earth’s magnetic field that emerges from the Earth’s dielectric centre defends against the solar wind.
Since both Earth and humans rely on solar energy any change in the intensity of the solar wind impacts the Earth and humans like how our close one’s behavioural change affects us. If you wanna know about the human dis-eases caused by the solar wind, you can refer here.
Reference
1. Ken Lee Wheeler. (2014). Uncovering the Missing Secrets of Magnetism. Darkstar publications.
2. Mar 18, 2024, NASA Science Editorial Team, Earth’s Magnetosphere: Protecting Our Planet from Harmful Space Energy, https://science.nasa.gov/science-research/earth-science/earths-magnetosphere-protecting-our-planet-from-harmful-space-energy/
3. January 04, 2024, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Solar wind, Diane K. Fisher, Nancy J. Leon, https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/nmp/st5/SCIENCE/solarwind.html
4. January 04, 2024, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, How magnetic storms form, Diane K. Fisher, Nancy J. Leon, https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/nmp/st5/SCIENCE/disturbances.html
5. Akasofu, SI. Auroral Substorms: Search for Processes Causing the Expansion Phase in Terms of the Electric Current Approach. Space Sci Rev 212, 341–381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0363-7
6. Liou, K., Sotirelis, T., & Mitchell, E. J. (2018). North-South Asymmetry in the Geographic Location of Auroral Substorms correlated with Ionospheric Effects. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35091-2
7. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Science Mission Directorate. (2010). The Earth’s Radiation Budget. Retrieved [October 06, 2024], from NASA Science website: http://science.nasa.gov/ems/13_radiationbudget
8. July 26, 2023, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Science on the Cusp: Sounding Rockets Head North, Miles Hatfield, https://www.nasa.gov/solar-system/science-on-the-cusp-sounding-rockets-head-north/
9. National Ocean Service. The Coriolis Effect. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/education/tutorial_currents/04currents1.html
10. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Global Atmospheric Circulations. U.S. Department of Commerce. https://www.noaa.gov/jetstream/global/global-atmospheric-circulations#:~:text=Polar%20cell%20%E2%80%93%20At%20higher%20latitudes,pressure%20called%20the%20polar%20highs.
11. Alabdulgader, A., McCraty, R., Atkinson, M., Dobyns, Y., Vainoras, A., Ragulskis, M., & Stolc, V. (2018). Long-Term Study of Heart Rate Variability Responses to Changes in the Solar and Geomagnetic Environment. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20932-x
12. Mavromichalaki, H., Papailiou, M., Gerontidou, M., Dimitrova, S., & Kudela, K. (2021). Human Physiological Parameters Related to Solar and Geomagnetic Disturbances: Data from Different Geographic Regions. Atmosphere, 12(12), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121613
13. Iheanacho F, Vellipuram AR. Physiology, Mechanoreceptors. [Updated 2023 Sep 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541068/
14. Song, Y., & Lysak, R. L. (2023). A mechanism of the auroral substorm expansion onset: Electric discharge in the double layer. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 10, 1296626. https://doi.org/10.3389/fspas.2023.1296626
No comments on this post so far:
Add your Thoughts:
Loading comments...